3-D Printing: The Future of Food?
3-D printing is the process of creating three-dimensional objects from a digital model. A traditional 3-D printer can intake a wide variety of materials ranging from liquids to powder. By giving specific commands to the computer, these materials can be fused in different ways, layer by layer. At this point, it is safe to say that 3-D printing has had a tremendous impact on all major sectors, globally. Be it mass production of industrial goods, designing clothes and intricate jewelry, or engineering the fastest of cars and computers.
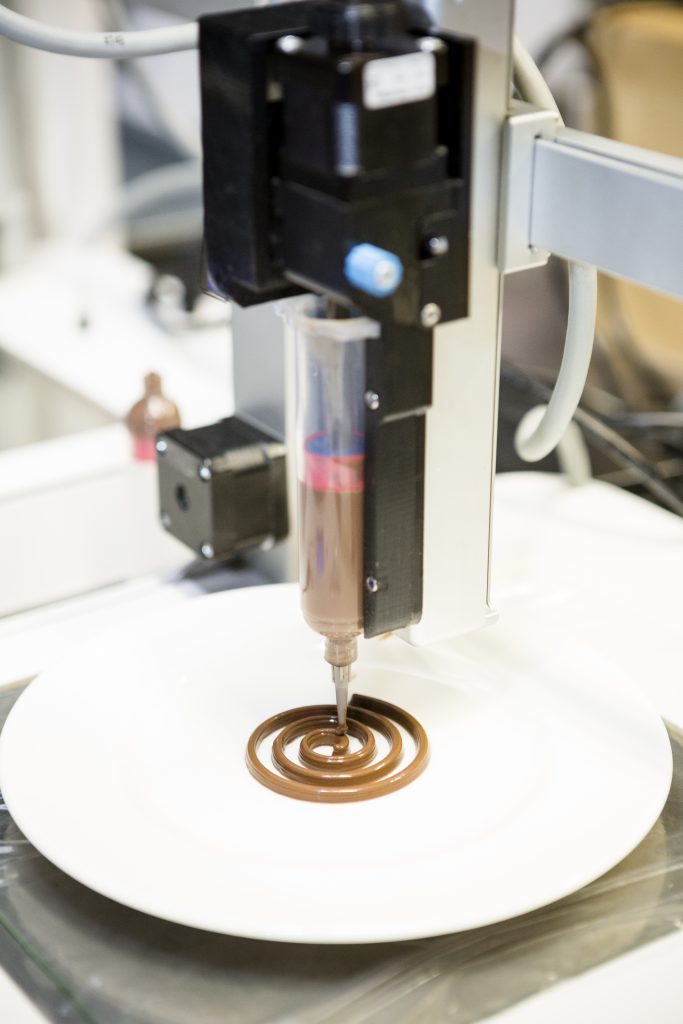
It is therefore not surprising that 3-D printing has also found its way into the food industry. In the simplest terms, 3-D printed food is a food prepared by automated means using a 3-D printer. Having said that, a 3-D printer does not actually cook the food. Processed or pre-cooked food items like jellies, mousses, purees, and other viscous foods are fed into a syringe-like container that has a nozzle that can trace the shape of the final object. This is done one layer at a time. It would sound like the options are limited, but combine different types of dessert fillings and batters, frostings, and cheeses, and the possibilities are endless. 3-D printed foods, if prepared under hygienic conditions and in clean machines, are absolutely safe to be consumed.
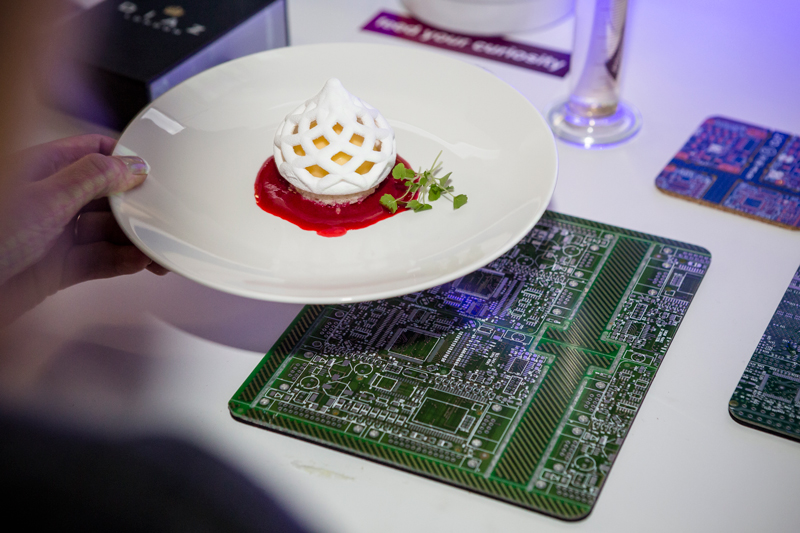
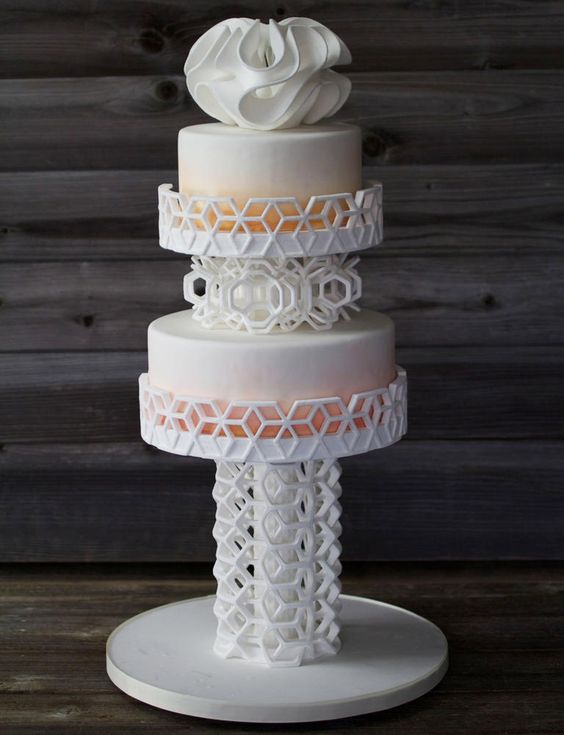
In recent times, 3-D printers are used in fancy restaurants and bakeries, mostly to garnish the food with stunning toppings that look too good to eat. A group of world-renowned chefs opened a restaurant in London called Food Ink that not only had 3-D printed food but also had the furniture made from a 3-D printer.
A pizza printing vending machine became very popular a couple of years ago. The machine was capable of making pizzas from scratch, from rolling the dough to adding your favorite toppings. Having said that, 3-D printed food is still in its initial stages. Like the pizza maker, a pancake bot came to the market that could make pancakes at the press of a button, and after adding the required raw materials, you only needed to flip it.

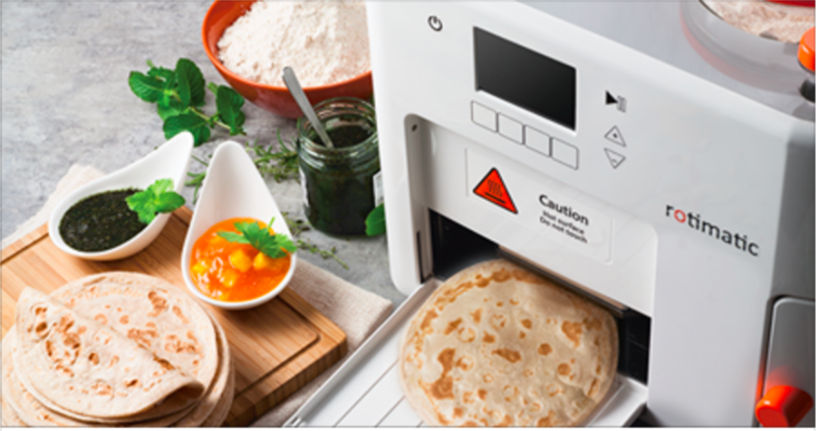
Roti, a traditional Indian flatbread made from flour, can also be made from a 3-D printer bot called Rotimatic. Another machine that made headlines was Foodini. It is capable of printing edible cake decorations, raw meat, and even stuffed pasta. It became very popular since it had a touch-based interface and users could connect to a cloud, where they could share their recipes with the community. However, it can only print food that needs further processing. It seems that the day when you will be able to create complex food, which looks like it has come straight out of your favorite food television show, in your own kitchen is not far away.

The advantages of printing food are many. This could be an excellent way to personalize your meals, keeping track of every nutrient, vitamin, and calorie that goes into each meal. This could be very useful in hospitals to prepare meals for patients with certain conditions. This technology could also be used to present food obtained from unconventional sources like protein-rich insects in an attractive way. Using 3-D printers, sharing recipes could be as easy as transferring a file.
Among the major drawbacks, one is time. For complex designs, the required time can be close to an hour. Another drawback is the cost. These machines are still not very common and mostly in the development phase. Therefore, the cost to manufacture is high. Since a lot depends on the starting raw material, reproducibility highly depends on how the starting material is prepared.
Many companies have planned to use these machines in several ways to revolutionize food. A few startups are trying to use 3-D printers to improve the texture of plant-based meats. Research is also underway to use 3-D printers to prepare meals for astronauts in space. Others are trying to utilize food waste and use that otherwise wasted food to make unique 3-D printed recipes. This could be very helpful in reducing food wastage. Not only food, but even plastic is being recycled as a material to 3-D print plates. The process of making synthetic foods is also underway. All in all, 3-D printing is going to change the way food will look in the future. It could be a great way to combat food shortage challenges around the world.
The day is not far when everyone will have a 3-D printer in their kitchens – what dish would you like to create?
Peer edited by Isabel Newsome